Enispect favours modular systems that can process various quantities of waste depending on the needs (from 2 tons of waste per hour).
Enispect offers solutions based on the latest technological advances in reactor design and catalyst development; whether the produced syngas is intended as generator/boiler fuel or for the production of green hydrogen.
Advantages to our approach include:
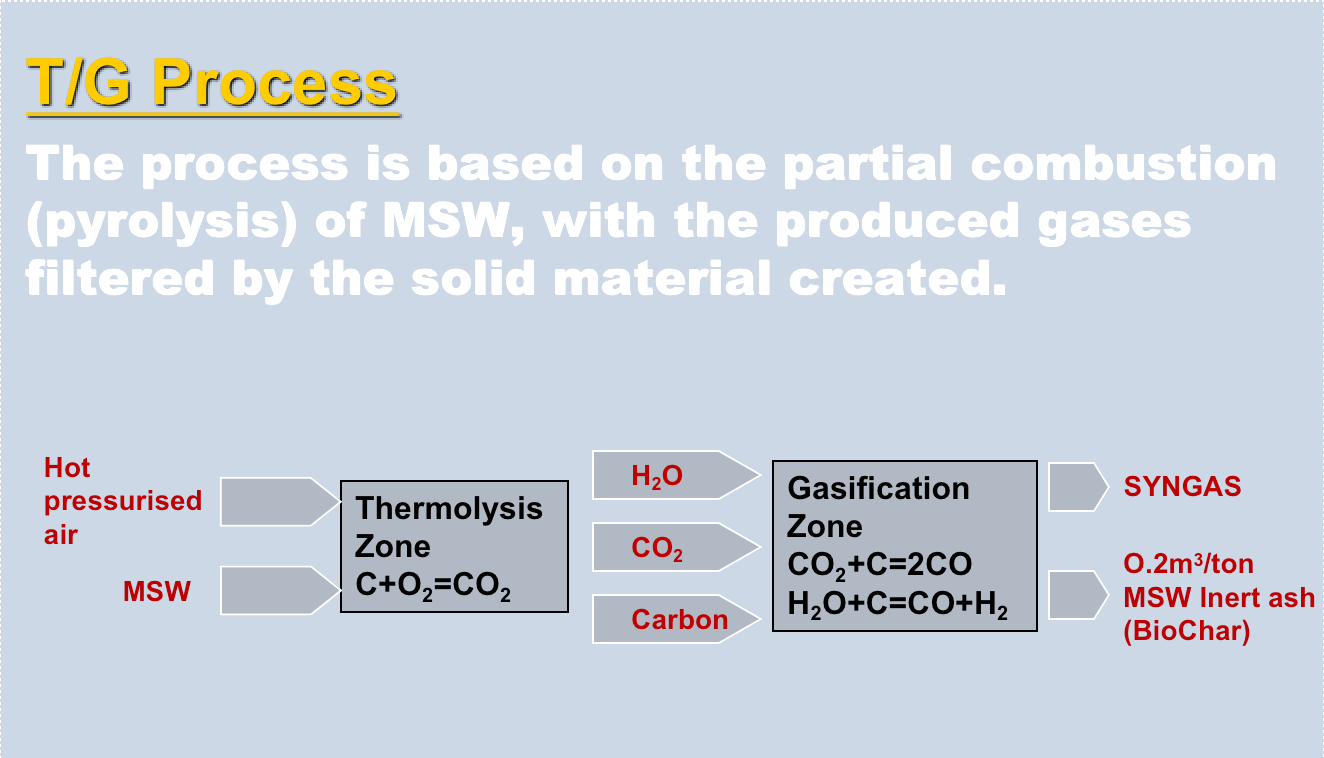
T/G produces:
Biochar: - A nutrient rich, inert and ash-like solid material; and may be used as a soil conditioner
SYNGAS
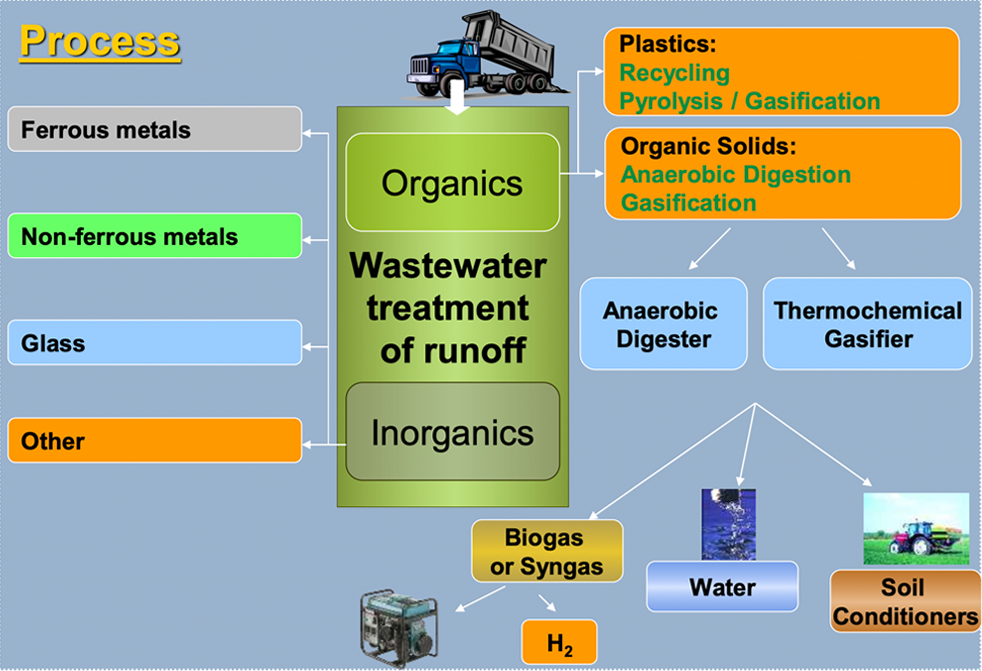
Latest technologies – more efficient, lower costs, applicable to food waste, plastics and other non-toxic organic materials (including wastewater treatment sludge, agricultural slurries etc.).
Based on the principle of thermolysis (thermochemical gasification –organics naturally breakdown into simpler organics when exposed to high temperatures in the absence of oxygen).
Breaks down organic materials into a synthetic gaseous fuel with Hydrogen and carbon monoxide being its main components
Anaerobic digestion (AD) is a biological process where volatile organics is biodegraded (digested) in an enclosed tank/reactor under anaerobic conditions (i.e. in the absence of oxygen), resulting in the production of a gas mixture (biogas) of methane (CH4) and carbon dioxide (CO2). Biogas is similar to natural gas, with the main difference being the proportions of CH4 and CO2, being typically 55%-70% CH4 and 45%-30% CO2., with natural gas having a much higher proportion of CH4 (>85%) and of course a lower proportion of CO2.
With the latest technology advancements, it is today possible to upgrade biogas to be very similar to natural gas.
AD can be used for processing any volatile organic matter, including food waste, biological sludge and livestock waste (e.g. poultry farms, pig farms, cattle farms, etc.) in many countries of the world.
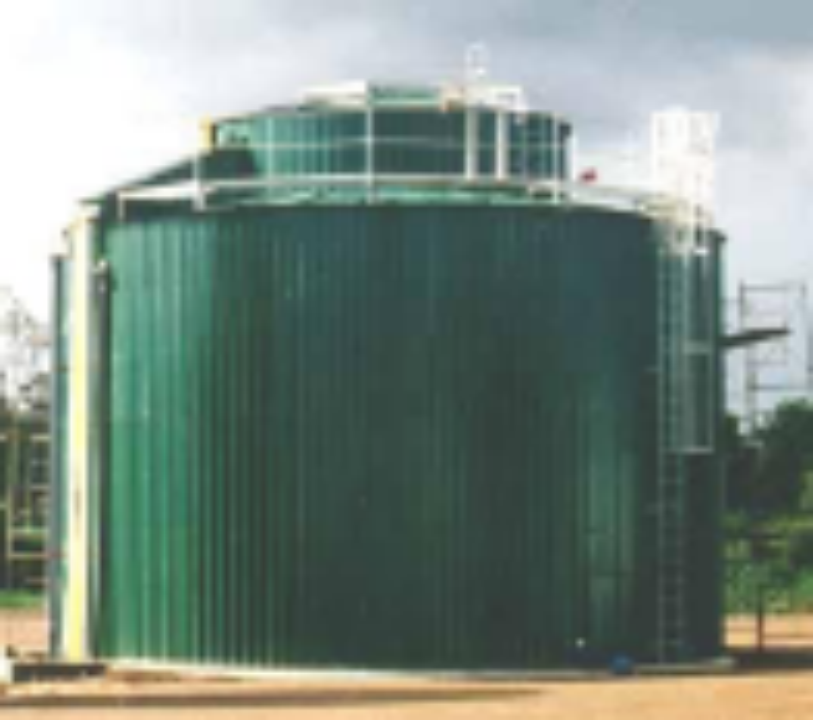

It is estimated that more than 5 million biogas plants are currently operating around the world, majority of which are small low-tech systems, but with several large scale high-tech systems also in operation.
AD is considered as one of the best available techniques (BAT), as it is an efficient renewable energy technology and highly reliable.
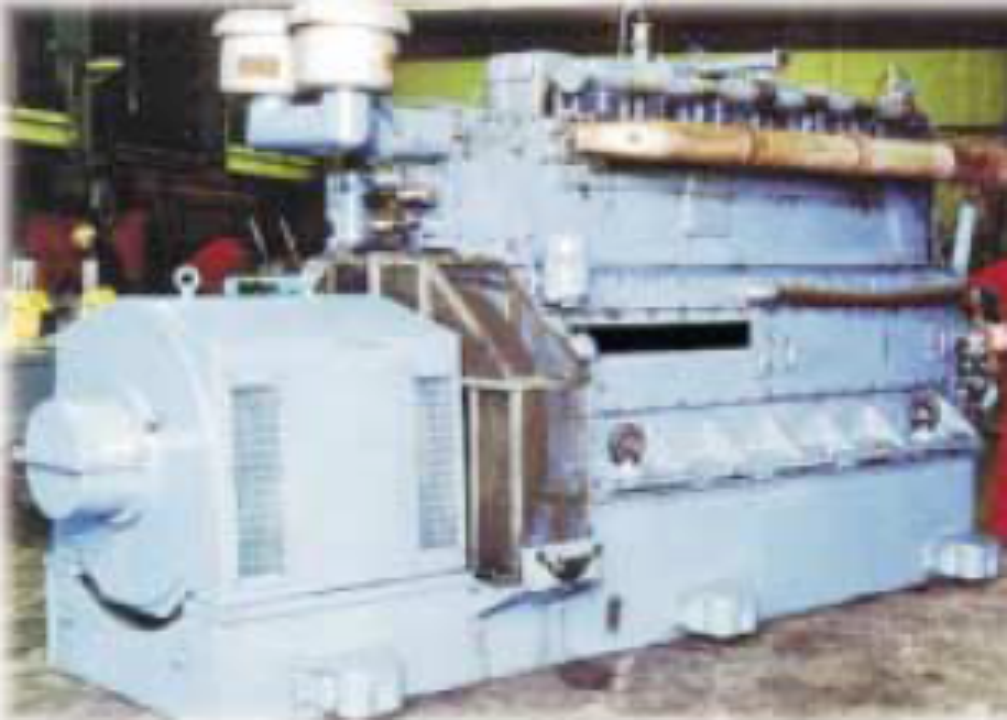
In most cases, biogas is used as an alternative green fuel for heat or electricity. For instance, in China where there are hundreds of thousands of small low-tech systems in operation, where the gas is used for cooking and heating of homes. On the other hand, biogas produced by large high-tech AD systems, is used a generator fuel to produce electricity and heat (cogeneration).
Biogas can also be broken down to H2 and CO, by steam reforming (a specialised version of the thermolysis process).
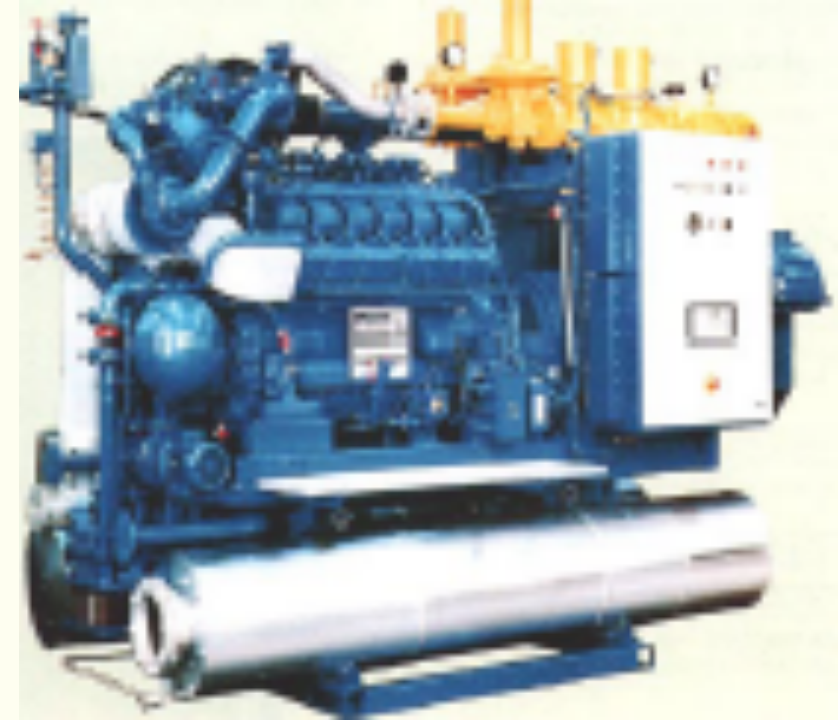

The most notable benefits of AD are outlined below:

6,154
2,512
5,980
Live Green, Love Green, Think Green.